Today (November 10th) morning, National Cultural Heritage Administration held a press conference on the progress of the major project "Archaeological China" in Beijing, and reported the latest achievements and progress in the archaeology of Yin Ruins and the study of Oracle Bone Inscriptions.
I. Archaeological Discovery and Research of Yin Ruins
Yin Ruins, located in Anyang City, Henan Province, are the ruins of the capital in the late Shang Dynasty. Since 1928, archaeologists in China have begun to carry out scientific archaeological excavations of Yin Ruins, which has opened the curtain of modern archaeology in China. Up to now, more than 90 years have passed, and important relics such as the palace area, residence area, tomb area, handicraft workshop area of Yin Ruins have been discovered one after another, as well as the neighboring Huanbei Mall, the capital of the middle Shang Dynasty, and a large number of precious cultural relics such as Oracle Bone Inscriptions, bronzes, pottery and jade wares have been unearthed. The distribution and structural layout of Yin Ruins were basically cleared up, and the chronological system of Yin Ruins culture was established, which provided a basis for exploring the archaeological culture of the early Shang Dynasty and even the Xia Dynasty. The research on the capital system, tomb system, sacrifice system, handicraft production system, architecture, water conservancy, spiritual belief and other aspects of the Shang Dynasty continued to deepen, demonstrating the history of the Shang Dynasty recorded in the literature and systematically showing the social and cultural features and the development achievements of the Shang Dynasty civilization. In 2006, Yin Ruins was listed in the World Heritage List, and its outstanding universal value was generally recognized by the international community, which provided a strong support for enhancing national self-confidence.

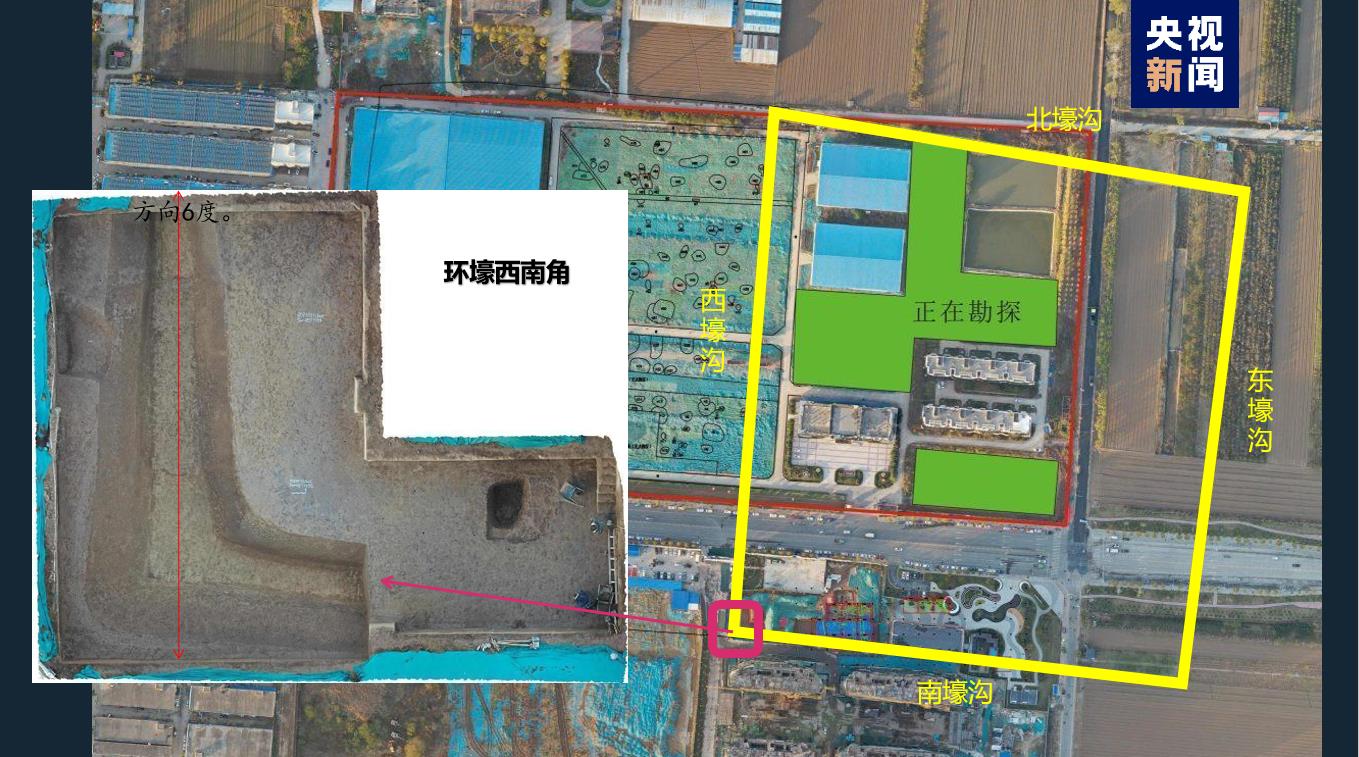
The archaeology of Yin Ruins has entered a new era and stage. Under the guidance of the concept of settlement archaeology, it has deepened the multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary cooperative research and made new breakthroughs. A large number of relics of copper casting, bone making, pottery making, living and living, and well-distributed cemeteries were found in the workshop area of Huanbei handicraft industry, which revealed the layout mode of "residence and burial in one" integrating production, life and funeral, and vividly displayed the production picture of handicraft industry in Shang Dynasty. Large ponds, waterways and related architectural relics have been newly discovered in the ancestral temple area of Xiaotun Palace, covering an area of more than 60,000 square meters. The ponds are connected with Huan River through waterways, which has changed the previous understanding of the overall pattern of the ancestral temple area of Yinxu Palace. Based on the exploration and excavation around the tomb area of Yin Ruins, it is confirmed that the eastern part and the western part of the tomb area are surrounded by a trench with a width of more than 10 meters, and the tomb and a large number of sacrificial pits are located in the trench. The discovery of the trench breaks through the understanding of the layout of the tomb area of Yin Ruins and is a major progress in the study of the cemetery system in Shang Dynasty. The road system inside the Yin Ruins has been continuously revealed. Two north-south roads leading directly to the palace area were found about 1km south of the ancestral temple area of the Yin Ruins, and a large road with a width of 15m was excavated on the north bank of Huanhe River. There were clear rutting marks on the roads, and residential areas, tombs, handicraft workshops and so on were densely distributed on both sides of the roads. The framework system revealed by the roads provided important clues for further exploring the urban layout and ethnic distribution of the Yin Ruins. Under the guidance of new ideas and methods, the archaeological research of Yin Ruins will gradually restore a more comprehensive, real and vivid Shang civilization.
Second, the new archaeological discoveries of settlements around Yin Ruins
Henan Province and Anyang City have implemented the policy of "archaeology first, then transferring" and actively strengthened the archaeological and cultural relics protection work in urban capital construction, and achieved many important achievements in the archaeological work of capital construction around Yin Ruins, greatly expanding the breadth and depth of archaeological research in Yin Ruins.
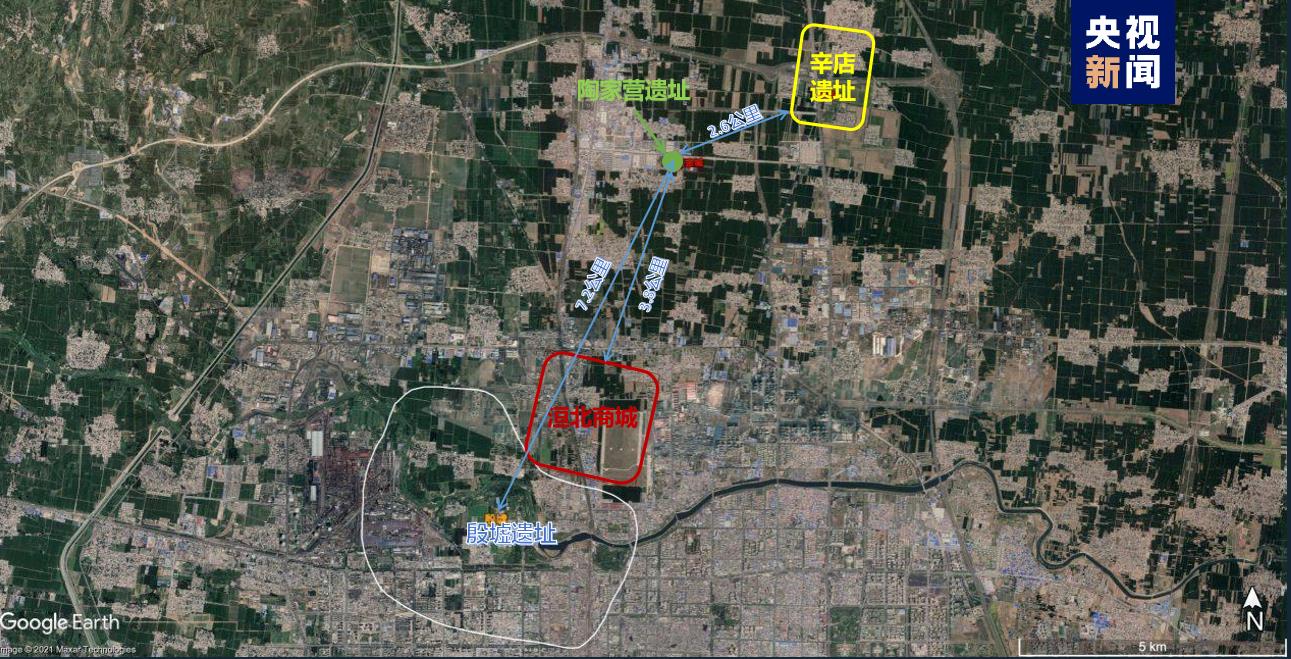
Xindian site, located about 10 kilometers north of Yinxu Palace, is a bronze casting site. Seven bronze casting workshops, more than 10 houses and nearly 100 tombs have been found in the late Shang Dynasty, and about 40,000 pieces of pottery models, pottery molds and a large number of tools for making models and casting copper have been unearthed. The unearthed bronzes bear the inscription "Ge", indicating that the site may be a bronze casting site managed by the "Ge" clan.




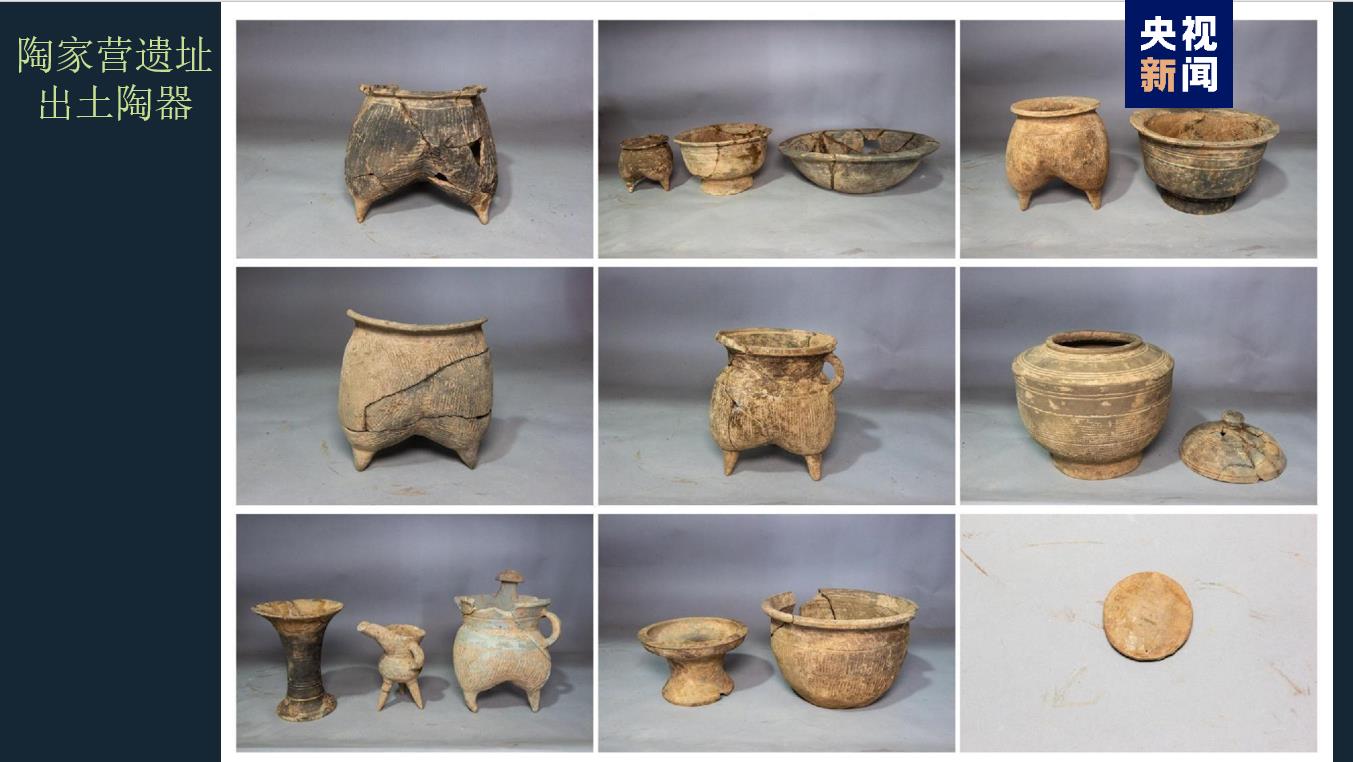
Taojiaying site is located about 7.2km north of Yinxu Palace. It is a moat settlement in the middle of Shang Dynasty. Pottery production area, residence area and tomb area were found in the site, and rich bronzes, jade articles and pottery were unearthed in 25 tombs, which further enriched the social research content of settlements around Huanbei Mall in the middle of Shang Dynasty.
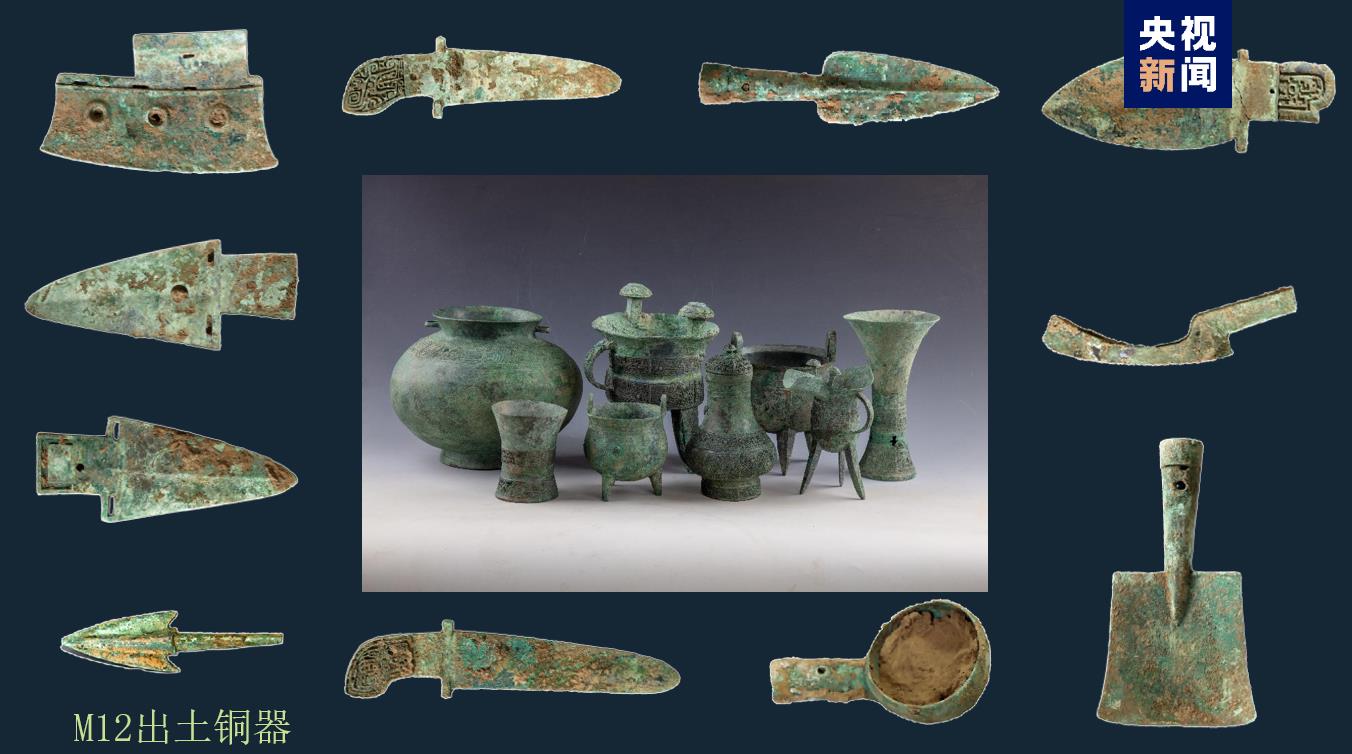


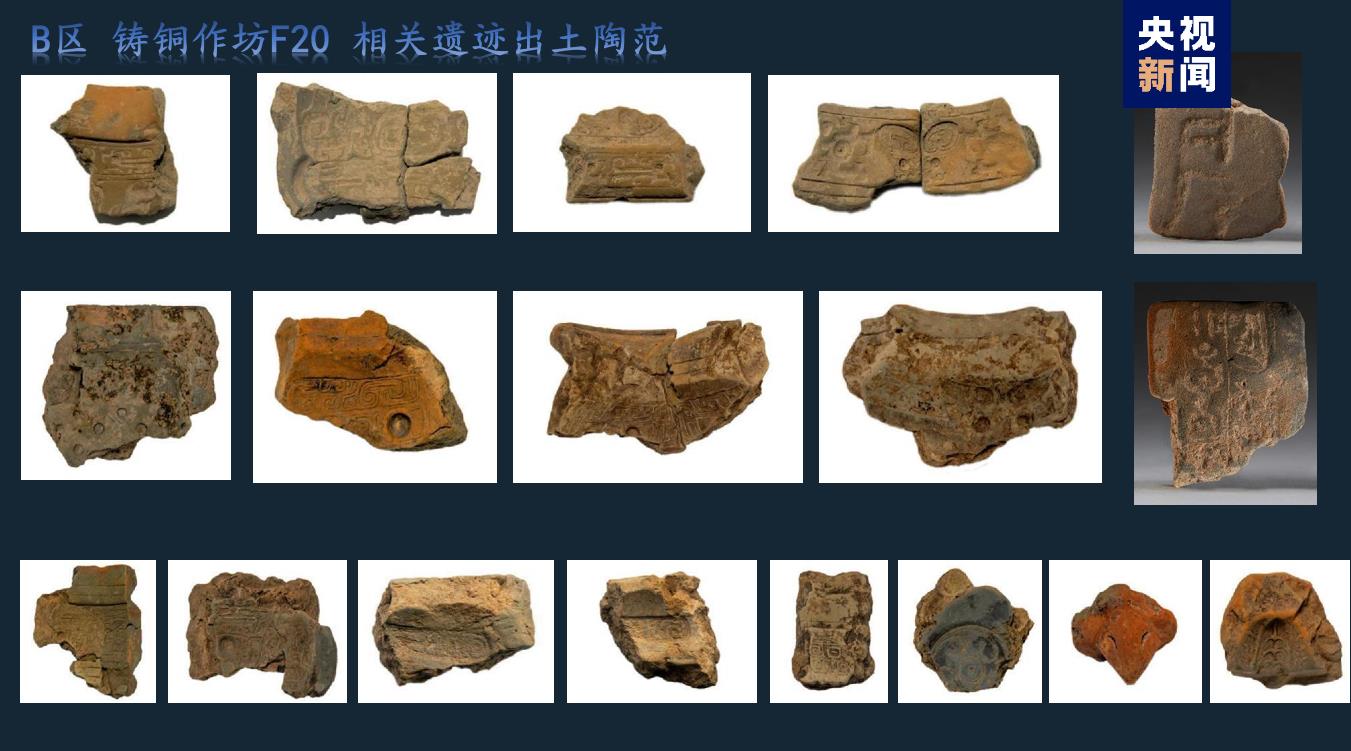
Shaojiapeng site, located about 2.5km south of the palace area of Yin Ruins, is a settlement in the late Shang Dynasty. Three groups of multi-entry courtyards consisting of 18 houses and a graveyard consisting of a Chinese-shaped tomb, 23 small and medium-sized tombs and 4 chariots and horses pits were found in the site. Many bronzes with the inscription "Book" were unearthed in the tombs, indicating that Shaojiapeng site may be the "Book" of historians in the late Shang Dynasty.
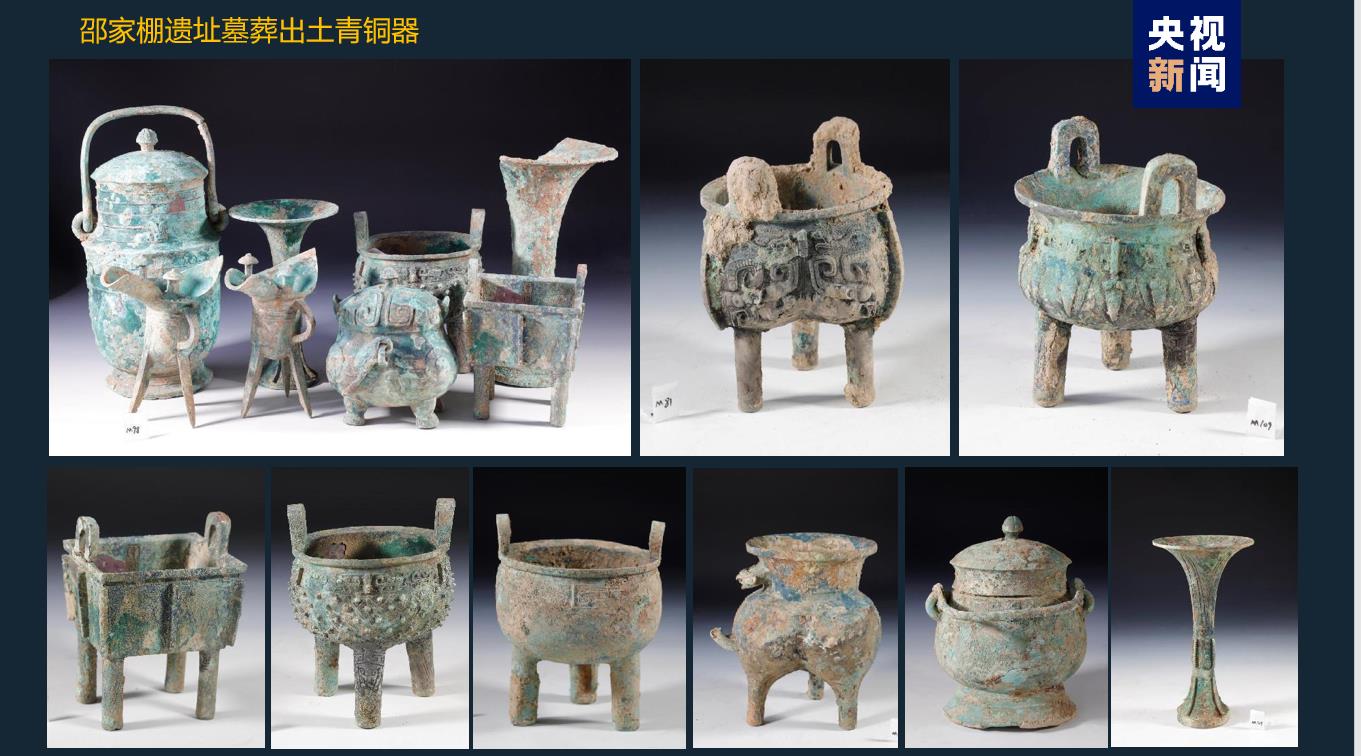
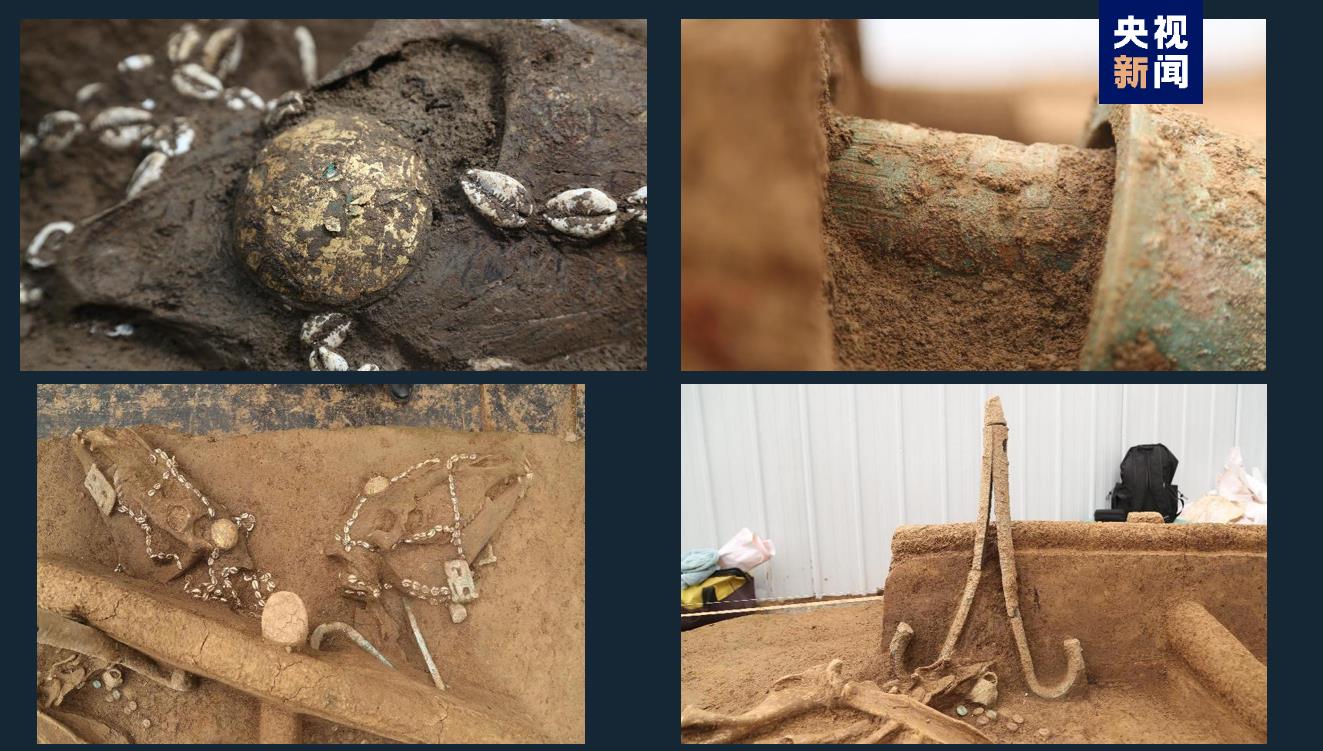




Third, Oracle Bone Inscriptions’s discovery and research
Oracle Bone Inscriptions is the representative of the early mature Chinese character system, and it is also the demonstration of Yin Ruins as the capital of Shang Dynasty. Oracle Bone Inscriptions was unearthed in Xiaotun Village, Anyang, Henan Province in the late Qing Dynasty. Up to now, about 150,000 pieces have been discovered, and more than 35,000 pieces have been scientifically excavated. The number of words has exceeded 4,000, covering all aspects of politics and life in Shang Dynasty, and it is the direct historical data for rebuilding the history of Yin and Shang Dynasties. There are three important discoveries of Oracle bones in Yin Ruins, namely, the largest number of intact pit YH127 in Xiaotun, the Oracle bones in the south of Xiaotun with a clear date, and the Oracle bones in the east of Garden Village in Yin Ruins with unique historical value. Oracle bones in Yin Ruins directly confirmed the existence of Shang Dynasty in ancient historical records, and Xiaotun in Anyang was Wang Ting of Yin Shang Dynasty, which advanced the upper limit of China’s trust history by more than 1000 years, opened the archaeological and historical research course of Yin Ruins for more than 90 years, and promoted the innovation and development of China’s traditional philology.

More than 120 years’ research on Oracle Bone Inscriptions has yielded fruitful results in Oracle Bone Inscriptions’s data collation, chronology by stages, textual research, business history research, compilation and publication of reference books, and personnel training. Based on the profound academic accumulation of more than a hundred years, the study of Oracle bones in the new era pays more attention to the combination with archaeological theories and methods and multi-disciplines, and has made important achievements in promoting the study of ideological history, astronomical calendar and historical geography, and solved the problem of digital divination, which is of breakthrough significance and value to the study of China’s traditional philosophy and ideological history. By reading the data of solar and lunar eclipses recorded by Oracle Bone Inscriptions and combining with astronomical deduction, the solar eclipse occurred on October 31, 1161 BC, which proved that Yin people had mastered the eclipse cycle, which was of great significance to the study of Oracle Bone Inscriptions dating and even the movement of the earth and the sun. Combined with Oracle Bone Inscriptions’s Oracle inscriptions and the inscriptions unearthed from the Shi family cemetery in Shangzhou, Tengzhou, Shandong Province, the landscape of Xue Guo in Shang Dynasty was determined, which provided a new fulcrum for the study of historical geography in Shang Dynasty. The study of Oracle Bone Inscriptions has developed into an international academic topic, with scholars participating in the study all over the world and numerous works, which have played an important role in promoting the spread of Chinese culture and promoting the exchange and mutual learning of civilizations.
(CCTV reporter Tian Yunhua Ren Meimei Zhang Leilei Guo Min)