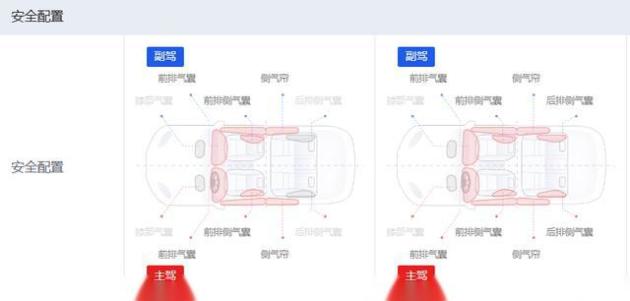
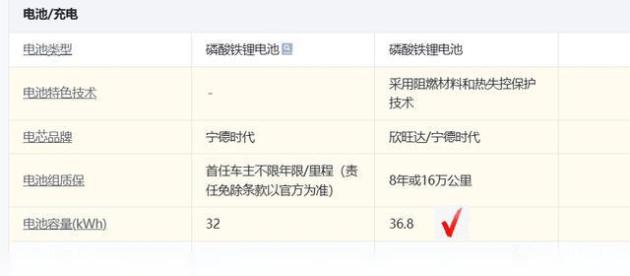
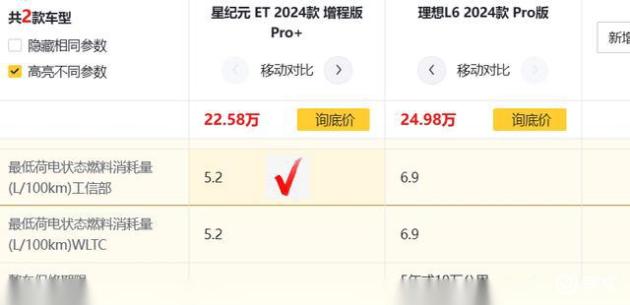
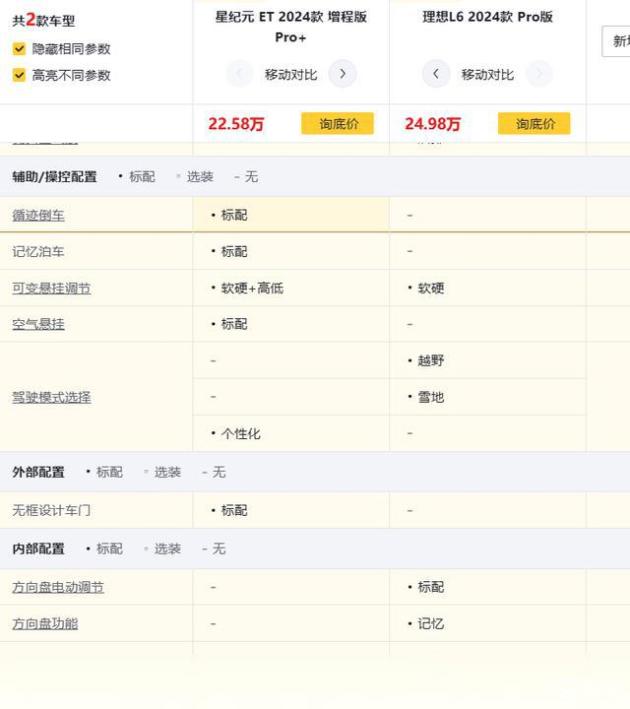
sequence726period | 2022/01/20



"This is our slogan, reading lights up life." Fan Deng said, pointing to the words printed on his T-shirt.
Fan Deng’s own life was actually lit up by reading.
Recalling the period when graduate students just graduated into CCTV, Fan Deng was very confused at that time, and his work pressure was great, his ability was not recognized, and his enthusiasm was nowhere to be displayed. "What if the program was shot again? What if I can’t afford the rent? " Fan Deng’s anxiety and insomnia are weighed down by realistic difficulties.
Rereading The Analects saved Fan Deng. He found that all the pains of contemporary people can be answered from this classic. As a student, the master of science and engineering who firmly believed that "learning mathematics and physics well and traveling all over the world are not afraid" suddenly found the key to solving the pain of life. It turns out that ending exam-oriented education and taking up jobs is not the end of learning, but the beginning of lifelong learning.

Fan Deng Image source: Every reporter Zhang Jianshe
Later, whether it was parenting, starting a business or managing a company, Fan Deng felt that reading helped him avoid detours. He teaches leadership in EMBA class and earnestly "Amway" good books to students, but few people actually read them. Then tell the book to everyone, and those who are willing to listen will pay to join the group. As a result, he found this model very popular, which is the embryonic form of "reading in Fan Deng".
2022 is the ninth year of Fan Deng’s study. The number of APP users evolved from the book club has exceeded 50 million, and it is stable and profitable.
And Fan Deng, who is lit up by reading, can light up the readers by telling books?Learning and seeking knowledge undoubtedly benefit people a lot. Can you really make people learn and change by spending 365 yuan to buy a member to listen to a book for one year?

Fan Deng won the "Knowler of the Year" trophy.
Image source: Every reporter Zhang Jianshe
At the end of the year and the beginning of the year, Fan Deng came to the release site of "New Weekly’s annual cutting-edge list" to win the trophy of "Know the Molecules of the Year". After receiving the award, Fan Deng accepted an exclusive interview with a reporter from national business daily (hereinafter referred to as NBD).

Read books to others.
I knew it was a business model from the beginning.

In 1995, Fan Deng, a junior majoring in materials science at Xi ‘an Jiaotong University, attended a summer camp, during which a Hong Kong senior asked him, "Have you read The Analects?" Fan Deng said, "No, I’m afraid I can’t read it?" The senior recommended him to read The Analects of Confucius.
The Analects of Confucius does not talk about "learning from time to time" at the beginning, but "the origin of the world is light with two arms, so why bother to connect with the city in the world" (who would exchange losing his arms in order to get the world? The fame and fortune in the world, why do people take it so seriously? )。 This book helped Fan Deng knock on the door of The Analects. Who would have thought that the Analects of Confucius later became a lamp to illuminate Fan Deng in the dark. He was born in science and engineering and worked as a CCTV host, and found his real enthusiasm and business opportunities in the lecture.

Reading lights up life, which is slogan who studies in Fan Deng.
Image source: Weibo, Fan Deng
NBD: As a person who loves reading, how did you first come up with the form of telling books?
Fan Deng:It is anxious to see others not reading. My own habit is to look for books to read when I encounter any problems. If I can’t host the program, I will read the books that host the program. Read books with children without taking them; Read leadership books without taking the team. "Studying in Fan Deng" is my first time to start a business. If I can’t start a business, I’ll read a business book.A question, after reading more than a dozen books, can basically be understood. I rely on reading for parenting, making money and management, and reading has benefited me the most.
Later, when I was a teacher in a university, I taught EMBA classes and found that the books recommended to students only bought and didn’t read. I will share the books I have read with them as PPT, but they don’t even read PPT, so I will start a WeChat group and talk about 50 books a year. The annual fee for joining the group is to press the voice button for 60 seconds and 60 seconds.
NBD: What node can it be found to be a business model?
Fan Deng:From the beginning, I knew it was a business model, because it was completely in line with the structure of an enterprise, and the services it provided could help people solve problems. Its marginal cost of communication was very low, and there was a repurchase rate. The CEO of our company is an EMBA student in the first batch of WeChat reading groups.
NBD: You studied materials science in college, management science for graduate students, movies for doctors, debating competitions, being a host, being a university teacher, and now you are starting a business. It seems that every choice has not failed in the secular sense, and you are also very confident. Are these brought to you by reading? Or because of what?
Fan Deng:These are all after-the-fact interpretations, and they can also be understood as failures. You said that I had a smooth trip, which was just your projection, not the fact. The fact is that it doesn’t matter whether it is smooth or not, and there is no wrong choice. To understand the shaping of life by randomness. I was admitted to the university because of the family environment of science and engineering. My father instilled in me "learn math, physics and chemistry well" since I was a child. Graduate students are all graduate students with good grades, so I should take one. The doctoral degree is to solve the Beijing hukou. Are not designed in advance or particularly forward-looking.

Fan Deng, who played the debate in his early years. Image source: Weibo, Fan Deng
But one thing, I never gave up trying, never gave up studying, and never said, "Come on, I’ll just get along." When I entered CCTV, I couldn’t do many programs I wanted to do, but I exercised a lot of ability in the process of making samples.Therefore, life is not clear about success or failure, and it is good to enjoy your life.

Listening to books is unreliable?
It is the arrogance and prejudice of intellectuals.

Fan Deng believes in the power law. As long as 1,000 loyal members are willing to pay for his knowledge and recommend it to their families or employees, it will be a success. Some members have further become the agents of studying in Fan Deng. This company does not need to advertise, and people and word of mouth have become the natural distribution channels of knowledge products in Fan Deng.
NBD: Which is better, listening to books or reading by yourself?
Fan Deng:For most people, listening to books is much better than reading, because the books I talk about are basically books that are not easy for everyone to understand. Listening to books can sort out the context more quickly and enter this field.
When we were growing up, all teachers did one thing-telling books, but who spoke better. So you don’t have to be resistant to new things,Many intellectuals feel that listening to books is unreliable at first, and they think how good they are at reading. This is a kind of arrogance and prejudice.

Fan Deng, who is telling a book. Source: Weibo, Fan Deng
NBD: How did the price of 365 yuan a year come from?
Fan Deng:It’s easy to remember that 365 yuan is one yuan a day, and it’s not too much to charge one yuan a day. We have a product called "Fan Deng tells the Analects of Confucius", and we set up a punch-in training camp, that is, we pay 300 yuan to join the punch-in training camp. If we don’t stop punching once, we will refund the fee.
This is actually a charging mode, but the completion rate of this punch-in training camp can reach 96%, and almost everyone has to refund their fees in the end, but I am particularly happy because they followed me to learn the Analects from beginning to end. Many messages said that if you don’t punch in on the last day, you will find it useful to learn and don’t refund your fees. It shows that there are many people who are willing to learn, and it is enough for us to do business with these people.
NBD: Will this pricing change?
Fan Deng:I don’t know, maybe it’s free, but I don’t tend to be free. Free things just spend your time. And because it’s all free, you will only choose the part that interests you, but follow me, you can hear physics, entrepreneurship, history … and books that you think have nothing to do with yourself, and you won’t take the initiative to read.The essence of education is encounter with knowledge, and search and independent choice lose the possibility of encounter.
NBD: What are the criteria for choosing what books to talk about?
Fan Deng:We hope that more people will read better books and not make decisions based on the number of hits of this book. Because the user seems to vote with traffic, he thinks he likes listening to parenting books, but if he is pushed parenting books for a long time, he will not go with you, and he will feel boring slowly. We should explore the potential of everyone. People who like to listen to parenting can also understand philosophy and physics. This is what Confucius said, "A gentleman is not a tool", and our content is a completely anti-Internet algorithm.
Some time ago, we also put on the shelves the content of "The Power of Calculus". Many people think how dare you talk about such an unpopular content of calculus? I just think that it is precisely because there are few people who know calculus that we should talk about this book and let everyone know how important calculus is. The CEO of a big platform often chats with me, saying how do you sell serious content so well? Isn’t it just for entertainment and people who eat melons who like to watch it? I don’t think so. I think everyone has an upward pursuit. If I make those serious contents wonderful and easy to understand, someone will be willing to pay.

Fan Deng, who is telling a book. Source: Video screenshot

It’s good to be listed.
Can’t go public,It doesn’t hinder doing what should be done.

When you open a web page and search for the term "Fan Deng", the most common content that appears in your field of vision is "annual income of 1 billion yuan". In fact, this number is still increasing. In the "double 11" in 2021, Fan Deng made a membership promotion, and sold a total of more than 300 million membership fees a week. During the reading festival, the sales volume exceeded 400 million yuan. In any era, scholars who "will make money" are often the most able to stimulate the public’s nerves.
NBD: At present, the most praised by outsiders for studying in Fan Deng is that the annual income exceeds 1 billion yuan. Is this figure accurate? What is the revenue structure?
Fan Deng:We are a very transparent company, and we do not hide the company’s revenue figures.In 2020, it will be about 1 billion yuan, which will nearly double the growth during the epidemic.
We are actually a company that spreads knowledge with my personal IP brand as the core. In terms of revenue structure, at present, the biggest revenue segment of the company is definitely Fan Deng’s subscription products, "Listen to me for 365 days", with a large number of subscribers and a high renewal rate. Many users have followed it for 78 years, and this part of the revenue is very stable and has been growing slowly, accounting for 60%~70% of the total revenue.
In addition to my products, there is also "Extraordinary Intensive Reading", where experts from all walks of life are invited to give lectures, such as professors of philosophy department of Fudan University, parenting experts, partners of McKinsey and so on. In addition, we also have course business, publishing business and offline bookstore. We published about 100 kinds of books in 2021, and there are more than 200 offline bookstores nationwide.

Fan Deng’s famous reading teacher Image source: Fan Deng reading official website
NBD: Is this growth rate within expectations?
Fan Deng:Actually, it’s a little slower than I expected. Exponential organizations are growing very fast, and it is normal to reach hundreds of millions of users in almost three or four years, such as Tik Tok. Reading in Fan Deng is published by traditional education. Compared with these industries, it will appear that we are fast, but it is slow compared with the Internet.
NBD: In July, 2021, Shanghai Soybean Network Technology Co., Ltd., the main operator of Fan Deng Reading, completed the latest round of financing. Is it preparing for the listing plan?
Fan Deng:We just want to do the right thing, it’s good to be listed and we can develop further; We can’t go public, and it doesn’t prevent us from doing what we should do.

Personal IP growth will not slow down
Maintain anti-vulnerability and ensure sufficient cash flow.

Knowledge economy is like a besieged city. In the besieged city, countless fans regard Fan Deng as an idol of knowledge and are willing to pay for it; But outside the besieged city, once financing, it will always face the scrutiny of the capital market-how to eliminate the uncertainty caused by high dependence on personal IP and the sale of "non-standardized" products. When dealing with personal brands, some people make "retreat arrangements", while others choose "not to slow down".
NBD: For content companies that are highly dependent on personal IP, there will be many concerns in the capital market. What do you think?
Fan Deng:Our products are not personal IP products, but intellectual property products. If I don’t talk about new books now, the company’s income will also exist, because so many books I have talked about before are subscription products with long-term existence and long-term revenue.
Although we are a weekly program, there are 700 people in our team. In addition, personal IP is only the starting point of the company. Now we are developing a matrix product structure, with our own publishing business and offline bookstore, as well as our own shopping mall, curriculum business and vocational skills training school.
The rapid development of science and technology will replace many people’s careers. Since we see this trend, we should do vocational skills training. For example, it is difficult for take-away workers to deliver takeout all the time in the future, so we should create some jobs that are more valuable as they get older.

Offline Bookstore Image Source: Weibo, Fan Deng
NBD: With the development of other businesses, the revenue structure of the company will be more balanced?
Fan Deng:Although the income from listening to books accounts for the largest proportion at present, the growth rate of other sectors is very fast, and it is certain that they will exceed the income from listening to books in the future.
We will not deliberately slow down the growth of other businesses to cater to that ruler, nor will the growth of my own IP slow down.But we should also do other businesses faster, so that the company can develop healthily.
NBD: What do you think of the trend of knowledge payment?
Fan Deng:The market develops periodically, and it seems that knowledge payment is still a good track at present. While referring to the market, the company will also focus on the business it wants to do.
My wife runs a beauty salon. One day, she said that she saw an article analyzing the trend of the medical and beauty industry, so I said it was unnecessary. First of all, what you are doing is not the whole medical and beauty industry, and that trend has nothing to do with you; Secondly, that trend may not be accurate; Third, seeing more trends affects your initial heart, and the trend says that you don’t make money, then you are shaken?So we only do what we have to do, while maintaining anti-vulnerability and abundant cash flow.If there is a bigger black swan incident, which leads to a major setback for the company, we still have a larger choice and may even become better.

Reporter’s Notes |
When Lecture Room first appeared, there was also controversy.
The emergence of new things is always accompanied by controversy. When the lecture room appeared, there was a lot of controversy. Can serious knowledge be told in this way by laughing and cursing?
However, an intellectual said it well, whether talking about the Analects of Confucius or Historical Records, at least it stimulated more ordinary people’s interest in understanding and getting close to historical classics.
In the digital age, the ways of knowledge dissemination are becoming more and more diverse. Whether reading or listening to books, the effect of knowledge payment on everyone varies from person to person.
However, under the trend of entertainment first, it is a good thing that some people are willing to promote reading and serious reading, create diverse content and innovative reading forms, so that more people are interested in reading and users have more choices.
Reporter |Ding Zhouyang Wen Menghua
Edit |Dong Xingsheng Song Hong Cheng Peng Yi Qijiang
Vision |Shuai lingqian
Video editing |Zhang Jian
Typesetting |Dong Xingsheng Ma Yuan
| The copyright of this article belongs to"every headline"All |
Reprinting, editing, copying and mirroring are prohibited without permission.
If you need to reprint, please apply to this WeChat official account backstage and get authorization.

After Delta, the Omicron strain became a global epidemic.

national business daily